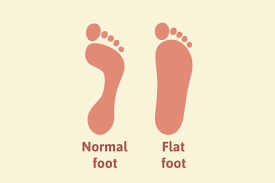
Flat feet, also known as pes planus, is a common condition where the arches of the feet are flattened, causing the entire sole of the foot to come into contact with the ground. In infants and young children, flat feet are a normal part of development as the arches typically develop during childhood. Most children naturally develop arches by the age of 6, but in some cases, flat feet may persist.
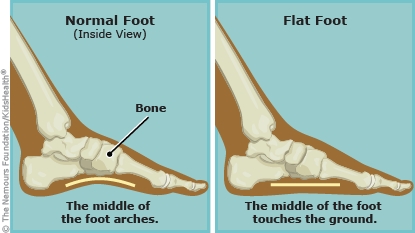
Here are some key points to consider:
- Normal Development:
- In infants and toddlers, it is normal for the arches of the feet to appear flat because the supportive tissues and tendons are still developing.
- As a child grows and begins to walk, the arches usually develop and the foot takes on a more typical shape.
- Common Causes of Persistent Flat Feet:
- Genetics: Flat feet can run in families.
- Loose ligaments: Some children have ligaments that are more flexible than usual, contributing to flat feet.
- Overpronation: Excessive inward rolling of the foot during walking.
- Neuromuscular conditions: Certain neurological or muscular conditions may lead to flat feet.
- When to Seek Medical Attention:
- If a child's feet remain flat beyond the age of 6, or if there are concerns about their walking pattern, it's advisable to consult with a pediatrician or a healthcare professional.
- Pain, discomfort, or difficulty with activities may be signs that warrant medical attention.
- Treatment and Management:
- In many cases, flat feet in children do not require specific treatment.
- If there is no pain or functional impairment, and the child is meeting developmental milestones, intervention may not be necessary.
- Orthotic devices or supportive shoes may be recommended in cases where there is discomfort or if the condition is affecting the child's activities.
- Monitoring and Follow-up:
- Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are important to monitor the child's foot development.
- If there are concerns about the child's gait, posture, or if they experience pain, further evaluation may be needed.
- Surgical Intervention (Rare):
- In severe cases or if flat feet are associated with an underlying condition, surgical intervention may be considered. However, this is relatively rare and typically reserved for cases with significant functional impairment.
It's crucial to remember that each child is unique, and the management of flat feet should be individualized based on the child's specific circumstances. Consulting with a healthcare professional, such as a pediatrician or a pediatric orthopedic specialist, can provide personalized guidance and recommendations for monitoring and managing flat feet in children.
Muffik Orthopaedic Sensory Mats are ideal tool to prevent or improve flat feet issues. Just few minutes a day can have incredible impact on your feet.